By Eric Vandenbroeck
and co-workers
What To Expect In 2023
The world is constantly changing, but some changes are
more critical than others. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine will likely be
remembered as the start of a new era in geoeconomics. In response to the war,
the West launched sanctions against Russia, escalating the economic war the
Kremlin began when it blocked Ukraine from trading with the world through its
ports. Moscow answered by drastically reducing natural gas exports to Europe.
The uncertainty and tit-for-tat measures kicked off an energy crisis. And the
war renewed focus on the growing divide between the West and a nascent
revisionist bloc led by China and Russia. It isn't easy to see a path back to
the status quo ante Bellum, but several significant trends that will define the
next decade have become clear.
Protectionism And Global Realignment
For years before
COVID-19, China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea challenged the economic,
financial, security, and geopolitical order the United States and its allies
created after World War II. The era of relentless globalization had started to
slow or even reverse. The pandemic kicked things into overdrive, accelerating
reshoring and so-called friend sharing and depriving developing economies of
foreign investment.
The war in Ukraine
and its economic aftereffects are squeezing developing countries even more. In
2022, most of them put off making a choice between the West and Russia, hoping
for a resolution to the conflict that would ease their economic pain. A case in
point is Hungary, which, like many of these countries, depends on Russian
energy and other commodities to sustain its economy and thus is wary of
breaking ties with Moscow. Budapest has sought to slow the progression of
Western sanctions against Russia. Others have avoided adopting anti-Russia
sanctions altogether.
For Europe, the
conflict between Russia and the West has shaken public and corporate confidence
about the near future and made it nearly impossible to do business with Russian
entities. Elsewhere, companies expend time and resources checking whether their
operations will incur sanctions, looking for alternatives whenever possible.
The Black Sea is a de facto war zone, with the upside of encouraging investment
in overland infrastructure and the downside of making maritime trade more
expensive.
As crucial as
European developments are, China and its internal stability may be the more
significant economic challenge in 2023. Facing growing protests late in the
year, the Chinese government abandoned its zero-COVID policy with no apparent
plan B. Official data is sparse and unreliable, and local and regional
governments have been put in charge of managing the situation. It is unclear
whether this will become a headache for Chinese leader Xi Jinping, especially
since it falls between the start of the political transition in November and
its end in March when most officials will have their new posts confirmed.
Meanwhile, the United States is escalating its trade war with China.
The result will
likely be a fragile economic recovery for China in 2023. The enduring weakness
of the real estate sector has outweighed positive impulses in other economic
areas, and fear of a financial crisis weighs on private investment. Increasing
youth unemployment adds a dangerous element to the mix. Beijing has taken steps
recently to solve the real estate sector’s liquidity crisis, but it needs
political stability for the measures to be effective.
This is not good news
for the global economy. As much as the West would like to be shielded from
events in China, Europe, and the U.S. still depend on Chinese manufacturing
essential inputs. Chinese lockdowns created kinks in supply chains, and the
country’s political and economic instability could prolong them. Consumption
and industrial activity in the U.S. and Europe are already in retreat, and
there’s no end to the energy crisis. A crisis in China would only make things
worse.
Stagflation And Greenflation
In addition to the
global economic slowdown, for the first time since the 1970s, the world is
simultaneously facing high inflation. The drivers of this bout of inflation
include excessively loose monetary and fiscal policies that were kept in place
for too long, the restructuring of global trade caused by the pandemic, and the
sharp spike in the cost of energy, industrial metals, fertilizers, and food as
a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Angered by the unequal distribution
of the gains of globalization, voters demanded more government support for
workers and those left behind. However well-intentioned, such policies risk an
inflationary spiral as wages and prices struggle to keep pace. Rising
protectionism also restricts trade and impedes the movement of capital,
limiting improvements on the supply side.
To the extent that
the energy crisis is causing high inflation, investment in renewables will
mitigate inflationary pressure. Renewable capacity will take time to develop,
however, and in the meantime, there is underinvestment in fossil fuel capacity.
The latter will take priority. Moreover, the green transition will require the
development of new supply chains for specific metals and will increase energy
costs generally, creating what’s been termed “reinflation.”
This coincides with a
rapidly aging population in developed countries, China, and other emerging
economies. Young people produce more, while older people spend their savings
and consume more services. And due to the market uncertainty caused by the
pandemic and the war in Ukraine, young people are producing less. They are
reluctant to invest, which translates into a general economic slowdown.
Therefore, just as the global economy will continue fragmenting into 2023, so
will inflation persist.
Future Of Tech
The war in Ukraine
has also disrupted the tech industry. While most sectors have been impacted by
declining investment and the challenging state of affairs, tech appears to be
the hardest hit. Twitter, for example, has cut its workforce by 50 percent, and
Facebook's parent company Meta is letting go of 11,000, about 13 percent, of
its employees. Amazon reportedly cut 10,000 jobs, representing about 1 percent
of its global workforce. Meanwhile, FTX, the second-largest cryptocurrency
exchange in the world, recently valued at $32 billion, has imploded. The full
fallout of its collapse is still unclear, but other crypto firms have already
felt the effects.
Gone are the days of
the early 2000s, when global markets were relatively stable, and supply chains
built on cheap labor were reliable. In those times, companies increasingly
depended on the internet to grow their business, and tech firms benefited from
low-interest rates. But the factors that helped propel the fast growth of the
early 2000s are today progressively volatile as the global economy hobbles
through the early stages of restructuring.
Like companies in
other sectors, many tech businesses won’t recover, while others will adapt and
bounce back slowly. New opportunities will arise. The restructuring of
manufacturing and supply chains will require technology, and automation will
increase, especially as the population ages. More critically, governments will
likely seize the opportunity to steer the tech industry in specific directions.
There has been much talk about social media's role in politics and shaping
policy. As a result, lawmakers have tried to regulate privacy and competition
related to social media platforms. Cybersecurity is also an increasingly
concerning issue for governments worldwide and will likely continue as the
sophistication of cyberattacks increases. Governments will therefore be pushed
to become more assertive in regulating tech beyond its military applications.
Geoeconomics For 2023
The major trends in
geoeconomics for 2023 and beyond are interconnected. The challenges they pose
will require a systematic, coherent approach, but the political leadership in countries
worldwide needs help to keep up. The speed of the change requires a different
toolset than governments are used to, leaving them trying, and sometimes
failing, to adapt to new realities. Cooperation is increasingly difficult, but
it has grown stronger in some limited areas, like the West’s economic war
against Russia following the Ukraine invasion.
Thus, even as deglobalization gains momentum,
interdependency isn’t going away. Restructuring itself will be a global
process. There’s no avoiding that the world today is interconnected in ways
never seen before. Different perspectives will need to be reconciled, and
people’s place in society beyond their economic value as consumers and
political value as voters will have to be acknowledged. Human behavior, and
therefore state behavior, is driven by everything from politics and economics
to culture and psychology and even technology. This complexity will navigate
tomorrow's challenges and potential solutions of tomorrow.
The world is
constantly changing, but some changes are more critical than others. Russia’s
invasion of Ukraine will likely be remembered as the start of a new era in
geoeconomics. In response to the war, the West launched sanctions against
Russia, escalating the economic war the Kremlin began when it blocked Ukraine
from trading with the world through its ports. Moscow answered by drastically
reducing natural gas exports to Europe. The uncertainty and tit-for-tat
measures kicked off an energy crisis. And the war renewed focus on the growing
divide between the West and a nascent revisionist bloc led by China and Russia.
It isn't easy to see a path back to the status quo ante Bellum, but several
significant trends that will define the next decade have become clear.
Protectionism And Global Realignment
For years before
COVID-19, China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea challenged the economic,
financial, security, and geopolitical order the United States and its allies
created after World War II. The era of relentless globalization had started to
slow or even reverse. The pandemic kicked things into overdrive, accelerating
reshoring and so-called friend sharing and depriving developing economies of
foreign investment.
The war in Ukraine
and its economic aftereffects are squeezing developing countries even more. In
2022, most of them put off making a choice between the West and Russia, hoping
for a resolution to the conflict that would ease their economic pain. A case in
point is Hungary, which, like many of these countries, depends on Russian
energy and other commodities to sustain its economy and thus is wary of
breaking ties with Moscow. Budapest has sought to slow the progression of
Western sanctions against Russia. Others have avoided adopting anti-Russia sanctions
altogether.
For Europe, the
conflict between Russia and the West has shaken public and corporate confidence
about the near future and made it nearly impossible to do business with Russian
entities. Elsewhere, companies expend time and resources checking whether their
operations will incur sanctions, looking for alternatives whenever possible.
The Black Sea is a de facto war zone, with the upside of encouraging investment
in overland infrastructure and the downside of making maritime trade more expensive.
As crucial as
European developments are, China and its internal stability may be the more
significant economic challenge in 2023. Facing growing protests late in the
year, the Chinese government abandoned its zero-COVID policy with no apparent
plan B. Official data is sparse and unreliable, and local and regional
governments have been put in charge of managing the situation. It is unclear
whether this will become a headache for Chinese leader Xi Jinping, especially
since it falls between the start of the political transition in November and
its end in March when most officials will have their new posts confirmed.
Meanwhile, the United States is escalating its trade war with China.
The result will
likely be a fragile economic recovery for China in 2023. The enduring weakness
of the real estate sector has outweighed positive impulses in other economic
areas, and fear of a financial crisis weighs on private investment. Increasing
youth unemployment adds a dangerous element to the mix. Beijing has taken steps
recently to solve the real estate sector’s liquidity crisis, but it needs
political stability for the measures to be effective.
This is not good news
for the global economy. As much as the West would like to be shielded from
events in China, Europe, and the U.S. still depend on Chinese manufacturing
essential inputs. Chinese lockdowns created kinks in supply chains, and the
country’s political and economic instability could prolong them. Consumption
and industrial activity in the U.S. and Europe are already in retreat, and
there’s no end to the energy crisis. A crisis in China would only make things
worse.
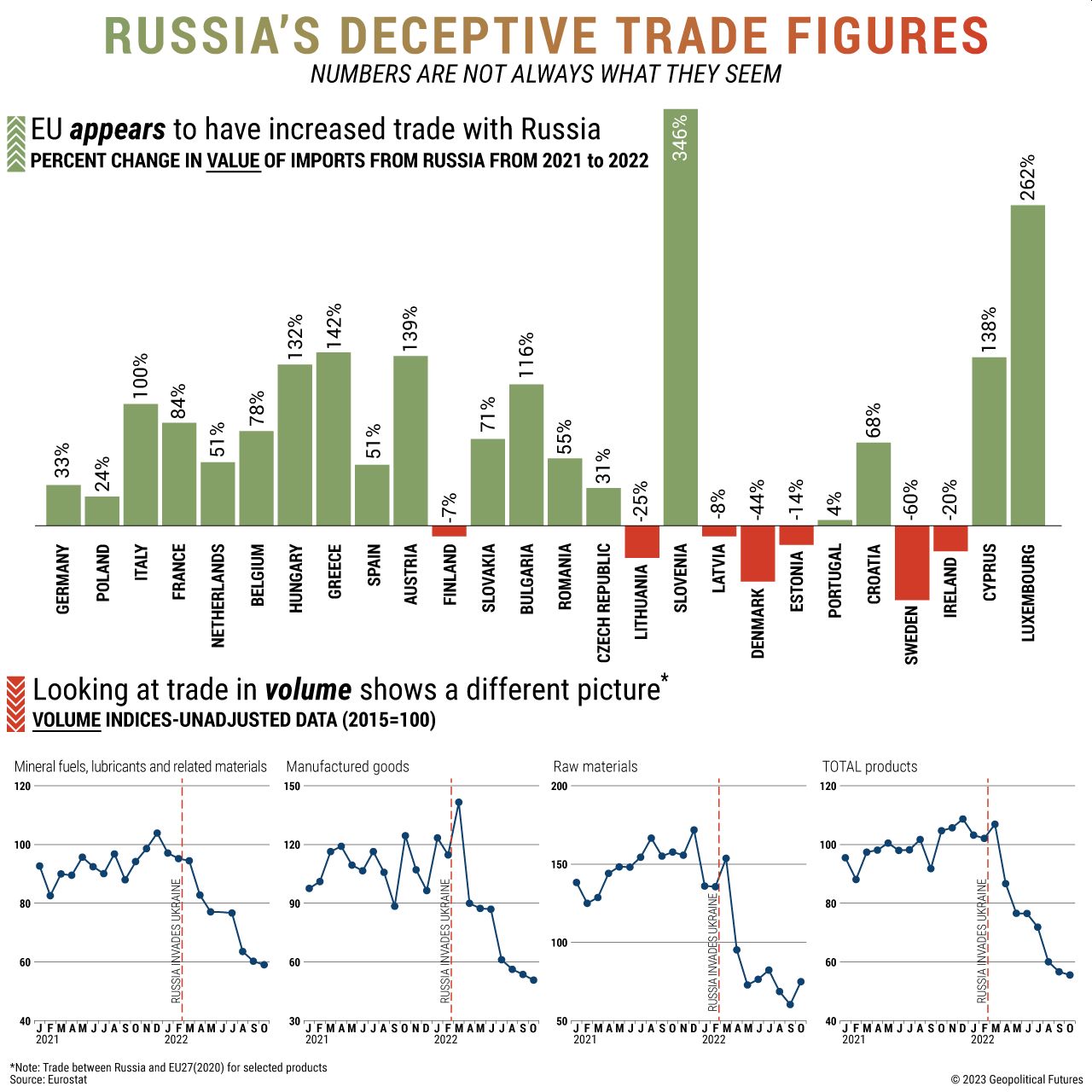
The sanctions imposed
by the West on Russia after its invasion of Ukraine precipitated a shift in
Russia’s trade patterns. The sanctions were meant to cut off economic ties with
Russia in Europe, but a complete severance was nearly impossible. As such, companies
in some sectors continued to do business with Russian firms at reduced levels
and at a more significant expense. The energy sector was hit particularly hard
by the changes. Energy prices soared, which had ripple effects for the rest of
the economy. The spike in the cost of Russian exports – especially oil and
natural gas – meant that the value of these exports to Europe increased. Still,
notably, the volume of Russian deliveries declined.
Notably, the value of
Slovenia’s and Luxembourg’s imports from Russia appears to have increased much
more than that of other European countries. This can be explained by the fact
that Russian exports to Slovenia are mostly energy products, and Russian
exports to Luxembourg are mainly metallurgical products, whose price is highly
dependent on energy costs.
As a result, the
overall value of Russian exports to Europe was higher in 2022 than in 2021,
despite Russia having sold fewer goods and services to European markets last
year. While the volume of exports of Russian raw materials to Europe has
fluctuated, exports in other segments are dropping, marking a shift that will
likely last for months and years to come as Europe finds alternatives.
For updates click hompage here