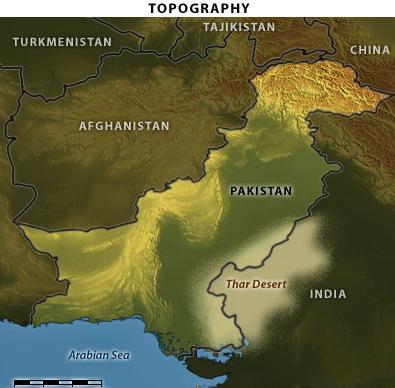
While Pakistan has
relatively definable boundaries, it lacks the ethnic and social cohesion of a
strong nation-state. Three of the four major Pakistani ethnic groups, Punjabis,
Pashtuns and Baluch, are not entirely in Pakistan. India has an entire state
called Punjab, 42 percent of Afghanistan is Pashtun, and Iran has a significant
Baluch minority in its Sistan-Baluchistan province.
Thus, the challenge
to Pakistan’s survival is twofold. First, the only route of expansion that
makes any sense is along the fertile Indus River Valley, but that takes
Pakistan into India’s front yard. The converse is also true: India’s logical
route of expansion through Punjab takes it directly into Pakistan’s core.
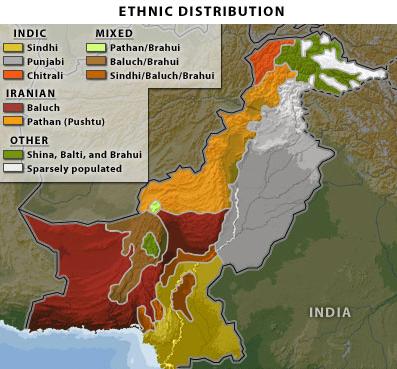
Second, Pakistan faces an insurmountable internal problem. In its efforts to
secure buffers, it is forced to include groups that, because of mountainous
terrain, are impossible to assimilate.
The first challenge
is one that has received little media attention of late but remains the issue
for long-term Pakistani survival. The second challenge is the core of
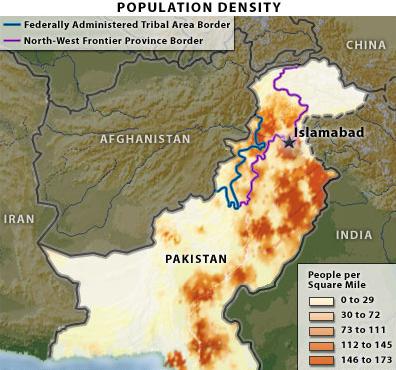
Pakistan’s “current” problems: The central government in Islamabad simply
cannot assert its writ into the outer regions, particularly in the Pashtun
northwest, as well as it can at its core.
The Indus core could
be ruled by a democracy, it is geographically, economically and culturally
cohesive, but Pakistan as a whole cannot be democratically ruled from the Indus
core and remain a stable nation-state. The only type of government that can realistically
attempt to subjugate the minorities in the outer regions, who make up more than
40 percent of Pakistan’s population, is a harsh one (i.e., a military
government). It is no wonder, then, that the parliamentary system Pakistan
inherited from its days of British rule broke down within four years of
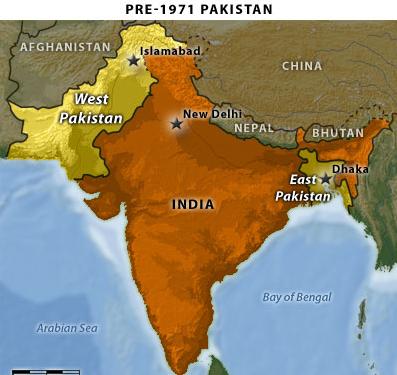
independence, which was gained in 1947 when Great Britain split British India
into Muslim-majority Pakistan and Hindu-majority India. After the 1948 death of
Pakistan’s founder, Mohammad Ali Jinnah, British-trained civilian bureaucrats
ran the country with the help of the army until 1958, when the army booted out
the bureaucrats and took over. Since then there have been four military coups,
and the army has ruled the country for 33 of its 61 years in existence.
While Pakistani
politics is rarely if ever discussed in this context, the country’s military
leadership implicitly understands the dilemma of holding onto the buffer
regions to the north and west. Long before military leader Gen. Mohammed
Zia-ul-Haq (1977-1988) began Islamizing the state, the army’s central command
sought to counter the secular, left-wing, ethno-nationalist tendencies of the
minority provinces by promoting an Islamic identity, particularly in the
Pashtun belt. At first, the idea was to strengthen the religious underpinning
of the republic in order to meld the outlands more closely with the core.
Later, in the wake of the Soviet military intervention in Afghanistan
(1978-1989), Pakistan’s army began using radical Islamism as an arm of foreign
policy. Islamist militant groups, trained or otherwise aided by the government,
were formed to push Islamabad’s influence into both Afghanistan and
Indian-administered Kashmir.
As Pakistan would
eventually realize, however, the strategy of promoting an Islamic identity to
maintain domestic cohesion while using radical Islamism as an instrument of
foreign policy would do far more harm than good.
Pakistan’s
Islamization policy culminated in the 1980s, when Pakistani, U.S. and Saudi
intelligence services collaborated to drive Soviet troops out of Afghanistan by
arming, funding and training mostly Pashtun Afghan fighters. When the Soviets
withdrew in 1989, Pakistan was eager to forge a post-communist Islamist
republic in Afghanistan, one that would be loyal to Islamabad and hostile to
New Delhi. To that end, Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) agency
threw most of its support behind Islamist rebel leader Gulbuddin Hekmatyar of Hizb i-Islami.
But things did not
quite go as planned. When the Marxist regime in Kabul finally fell in 1992, a
major intra-Islamist power struggle ensued, and Hekmatyar lost much of his
influence. Amid the chaos, a small group of madrassah teachers and students who
had fought against the Soviets rose above the factions and consolidated control
over Afghanistan’s Kandahar region in 1994. The ISI became so impressed by this
Taliban movement that it dropped Hekmatyar and joined with the Saudis in
ensuring that the Taliban would emerge as the vanguard of the Pashtuns and the
rulers of Kabul.
The ISI was not the
only one competing for the Taliban’s attention. A small group of Arabs led by
Osama bin Laden reopened shop in Afghanistan in 1996, looking to use a
Taliban-run government in Afghanistan as a launchpad for reviving the
caliphate. Ultimately, this would involve overthrowing all secular governments
in the Muslim world (including the one sitting in Islamabad.) The secular,
military-run government in Pakistan, on the other hand, was looking to use its
influence on the Taliban government to wrest control of Kashmir from India.
While Pakistan’s ISI occasionally collaborated with al Qaeda in Afghanistan on
matters of convenience, its goals were still ultimately incompatible with those
of bin Laden. Pakistan was growing weary of al Qaeda’s presence on its western
border, but soon became preoccupied with an opportunity developing to the east.
The Pakistani
military saw an indigenous Muslim uprising in Indian-administered Kashmir in
1989 as a way to revive its claims over Muslim-majority Kashmir. It did not
take long before the military began developing small guerrilla armies of
Kashmiri Islamist irregulars for operations against India. When he was a
two-star general and the army’s director-general of military operations, former
Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf played a leading role in refining the
plan, which became fully operational in the 1999 Kargil War. Pakistan’s war
strategy was to infiltrate Kashmiri Islamist guerrillas across the Line of
Control (LoC) while Pakistani forces occupied high-altitude positions on Kargil
Mountain. When India became aware of the infiltration, it sought to dislodge
the guerrillas, at which point Pakistani artillery opened up on Indian troops
positioned at lower-altitude base camps. While the Pakistani plan was initially
successful, Indian forces soon regained the upper hand and U.S. pressure helped
force a Pakistani retreat.
But the defeat at
Kargil did not stop Pakistan from pursuing its Islamist militant proxy project
in Kashmir. Groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), Hizb-ul-Mujahideen, Harkat-ul-Jihad-al-Islami, Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) and Al Badr
spread their offices and training camps throughout Pakistani-occupied Kashmir
under the guidance of the ISI. Whenever Islamabad felt compelled to turn up the
heat on New Delhi, these militants would carry out operations against Indian
targets, mostly in the Kashmir region.
India, meanwhile,
would return the pressure on Islamabad by supporting Baluchi rebels in western
Pakistan and providing covert support to the ethnic Tajik-dominated Northern
Alliance, the Taliban’s main rival in Afghanistan. While Pakistan grew more and
more distracted by supporting its Islamist proxies in Kashmir, the Taliban grew
more attached to al Qaeda, which provided fighters to help the Taliban against
the Northern Alliance as well as funding when the Taliban were crippled by an
international embargo. As a result, al Qaeda extended its influence over the
Taliban government, which gave al Qaeda free rein to plan and stage the
deadliest terrorist attack to date against the West.
The Post 9/11 Environment
On Sept. 11, 2001,
when the World Trade Center towers and the Pentagon were attacked, the United
States put Pakistan in a chokehold: Cooperate immediately in toppling the
Taliban regime, which Pakistan had nurtured for years, or face destruction.
Musharraf tried to buy some time by reaching out to Taliban leaders like Mullah
Omar to give up bin Laden, but the Taliban chief refused, making it clear that
Pakistan had lost against al Qaeda in the battle for influence over the
Taliban.
Just a few months
after the 9/11 attacks, in December 2001, Kashmiri Islamist militants launched
a major attack on the Indian parliament in New Delhi. Still reeling from the
pressure it was receiving from the United States, Islamabad was now faced with
the wrath of India. Both dealing with an Islamist militant threat, New Delhi
and Washington tag-teamed Islamabad and tried to get it to cut its losses and
dismantle its Islamist militant proxies.
To fend off some of
the pressure, the Musharraf government banned LeT and
JeM, two key Kashmiri Islamist groups fostered by the ISI and with close ties
to al Qaeda. India was unsatisfied with the ban, which was mostly for show, and
proceeded to mass a large military force along the LoC in Kashmir. The
Pakistanis responded with their own deployment, and the two countries stood at
the brink of nuclear war. U.S. intervention allowed India and Pakistan to step
back from the precipice. In the process, Washington extracted concessions from
Islamabad on the counterterrorism front, and official Pakistani support for the
Afghan Taliban withered within days.
The Devolution of the Secret Service (ISI)
The post 9/11
shake-up ignited a major crisis in the Pakistani military establishment. On one
hand, the military was under extreme pressure to stamp out the jihadists along
its western border. On the other hand, the military was fearful of U.S. and
Indian interests aligning against Pakistan. Islamabad’s primary means of
keeping Washington as an ally was its connection to the jihadist insurgency in
Afghanistan. So Islamabad played a double game, offering piecemeal cooperation
to the United States while maintaining ties with its Islamist militant proxies
in Afghanistan.
But the ISI’s grip
over these proxies was already loosening. In the run-up to 9/11, al Qaeda not
only had close ties to the Taliban regime, but also had reached out to ISI
handlers whose job it was to maintain links with the array of Islamist militant
proxies supported by Islamabad. Many of the intelligence operatives who had
embraced the Islamist ideology were working to sabotage Islamabad’s new
alliance with Washington, which threatened to destroy the Islamist militant
universe they had created. While the ISI leadership was busy trying to adjust
to the post-9/11 operating environment, others within the middle and junior
ranks of the agency started to engage in activities not necessarily sanctioned
by their leadership.
As the influence of
the Pakistani state declined, al Qaeda’s influence rose. By the end of 2003,
Musharraf had become the target of at least three al Qaeda assassination
attempts. In the spring of 2004, Musharraf, again under pressure from the
United States, was forced to send troops into the tribal badlands for the first
time in the history of the country. Pakistani military operations to root out
foreign fighters ended up killing thousands in the Pashtun areas, creating
massive resentment against the central government.
In October 2006, when
a deadly U.S. Predator strike hit a madrassah in Bajaur agency, killing 82
people, the stage was set for a jihadist insurgency to move into Pakistan
proper. The Pakistani Taliban linked up with al Qaeda to carry out scores of
suicide attacks, most against military targets and all aiming to break
Islamabad’s resolve to combat the insurgency. A major political debacle threw
Islamabad off course in March 2007, when Musharraf’s government was hit by a
pro-democracy movement after he dismissed the country’s chief justice. Four
months later, a raid on Islamabad’s Red Mosque, which Islamist militants had
occupied, threw more fuel onto the insurgent fires, igniting suicide attacks in
major Pakistani cities like Karachi and Islamabad, while the writ of the state
continued to erode in the NWFP and FATA.
Musharraf was forced to
step down as army chief in November 2007 and as president in August 2008,
ushering in an incoherent civilian government. In December 2007, the world got
a good glimpse of just how dangerous the murky ISI-jihadist nexus had become
when the political chaos in Islamabad was exploited with a bold suicide attack
that killed Pakistani opposition leader Benazir Bhutto. Historically, the
Pakistani military had been relied on to step in and restore order in such a
crisis, but the military itself was coming undone as the split widened between
those willing and those unwilling to work with the jihadists. Now, in the final
days of 2008, the jihadist insurgency is raging on both sides of the
Afghan-Pakistani border, with the country’s only guarantor against collapse,
the military, in disarray.
India has watched
warily as Pakistan’s jihadist problems have intensified over the past several
years. Of utmost concern to New Delhi have been the scores of Kashmiri Islamist
militants who had been operating on the ISI’s payroll, and who had a score to settle
with India. As Pakistan became more and more distracted with battling jihadists
within its own borders, the Kashmiri Islamist militant groups began loosening
their bonds with the Pakistani state. Groups such as LeT
and JeM, who had been banned and forced underground following the 2001 Indian
parliament attack, started spreading their tentacles into major Indian cities.
These groups retained links to the ISI, but the Pakistani military had bigger
issues to deal with and needed to distance itself from the Kashmiri Islamists.
If these groups were to continue to carry out operations, Pakistan needed some
plausible deniability.
Over the past several
years, Kashmiri Islamist militant groups have carried out sporadic attacks
throughout India. The attacks have involved commercial-grade explosives rather
than the military-grade RDX that is traditionally used in Pakistani-sponsored attacks,
another sign that the groups are distancing themselves from Pakistan. The
attacks, mostly against crowded transportation hubs, religious sites (both
Hindu and Muslim) and marketplaces, were designed to ignite riots between
Hindus and Muslims that would compel the Indian government to crack down and
revive the Kashmir cause.
However, India’s
Hindu nationalist and largely moderate Muslim communities failed to take the
bait. It was only a matter of time before these militant groups began seeking
out more strategic targets that would affect India’s economic lifelines and
ignite a crisis between India and Pakistan. As these groups became increasingly
autonomous, they also started linking up with members of al Qaeda’s
transnational jihadist movement, who had a keen interest in stirring up
conflict between India and Pakistan to divert the attention of Pakistani forces
to the east.
By November 2008,
this confluence of forces, Pakistan’s raging jihadist insurgency, the
devolution of the ISI and the increasing autonomy of the Kashmiri groups,
created the conditions for one of the largest militant attacks in history to
hit Mumbai, highlighting the extent to which Pakistan has lost control over its
Islamist militant proxy project.
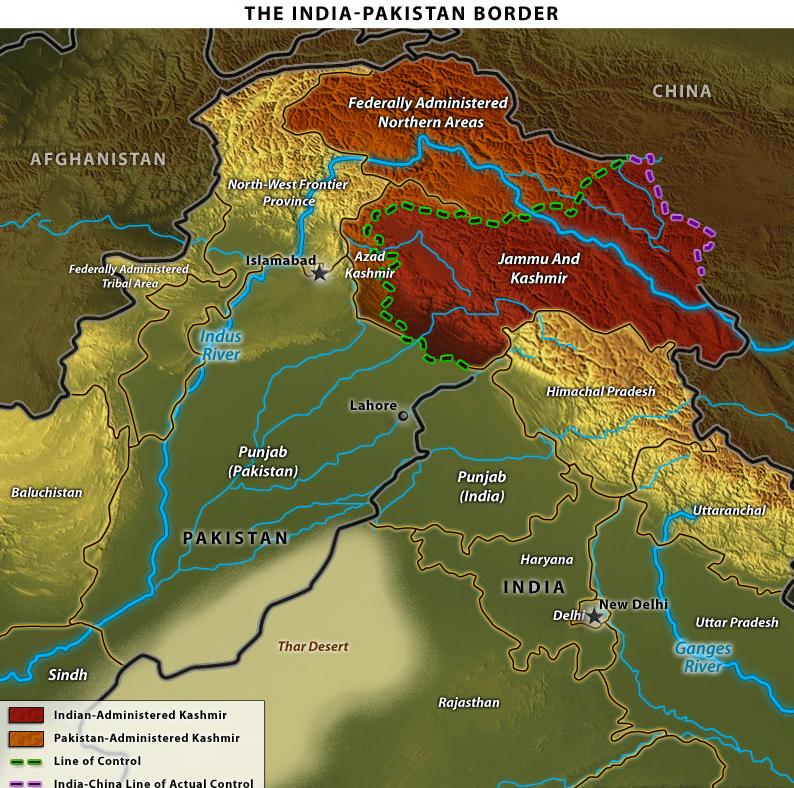
The India-Pakistan Rivalry
The very real
possibility that India and Pakistan could soon engage in what would be their
fifth war after nearly five years of peace talks is a testament to the
endurance of their 60-year rivalry. The seeds of animosity were sown during the
bloody 1948 partition, in which Pakistan and India split from each other along
a Hindu/Muslim divide. The sorest point of contention in this subcontinental
divorce centered around the Muslim-majority region of Kashmir, whose princely
Hindu ruler at the time of the partition decided to join India, leading the
countries to war a little more than two months after their independence. That
war ended with India retaining two-thirds of Kashmir and Pakistan gaining
one-third of the Himalayan territory, with the two sides separated by a Line of
Control (LoC). The two rivals fought two more full-scale wars, one in 1965 in
Kashmir, and another in 1971 that culminated in the secession of East Pakistan
(now Bangladesh.)
Shortly after India
fought an indecisive war with China in 1962, the Indian government embarked on
a nuclear mission, conducting its first test in 1974. By then playing catch-up,
the Pakistanis launched their own nuclear program soon after the 1971 war. The
result was a full-blown nuclear arms race, with the South Asian rivals devoting
a great deal of resources to developing and testing short-range and
intermediate missiles. In 1998, Pakistan and India conducted a series of
nuclear tests that earned international condemnation and officially nuclearized
the subcontinent.
Once the nuclear
issue was added to the equation, Pakistan became bolder in its use of Islamist
militant proxies to keep India locked down. Such groups became Pakistan’s
primary tool in its military confrontation, as the presence of nuclear weapons,
from Pakistan’s point of view, significantly decreased the possibility of
full-scale conventional war. Pakistan’s ISI also had a hand in a Sikh rebel
movement in India in the 1980s, and it continues to use Bangladesh as a
launchpad for backing a number of separatist movements in India’s restive
northeast. In return, India would back Baluchi rebels in Pakistan’s western
Baluchistan province and extend covert support to the anti-Taliban Northern
Alliance in Afghanistan throughout the 1990s.
Indian movements in
Afghanistan, a country Pakistan considers a key buffer state for extending its
strategic depth and guarding against invasions from the west, will always keep
Islamabad on edge. When Soviet troops invaded Afghanistan in 1979, Pakistan was
trapped in an Indian-Soviet vise, making it all the more imperative for the
ISI’s support of the Afghan mujahideen to succeed in driving the Soviets back
east.
Pakistan spent most
of the 1990s trying to consolidate its influence in Kabul to protect its
western frontier. By 2001, however, Pakistan once again started to feel the
walls closing in. The 9/11 attacks, followed shortly thereafter by a Kashmiri
Islamist militant attack on the Indian parliament, brought the United States
and India into a tacit alliance against Pakistan. Both wanted the same thing,
an end to Islamist militancy, and this time there was no Cold War paradigm to
prevent New Delhi and Washington from having a broader, more strategic
relationship.
This was Pakistan’s
worst nightmare. The military knew Washington’s post-9/11 alliance with
Islamabad was short-term and tactical in nature in order to facilitate the U.S.
war in Afghanistan. They also knew that the United States was seeking a
long-term strategic alliance with the Indians to sustain pressure on Pakistan,
hedge against Russia and China and protect supply lines running from the
oil-rich Persian Gulf. In essence, the United States felt temporarily trapped
in a short-term relationship with Pakistan while in the long-run, for myriad
strategic reasons, it desired an alliance with India. Pakistan has attempted to
play a double game with Washington by offering piecemeal cooperation in
battling the jihadists while retaining its jihadist card. But this is becoming
an increasingly difficult balancing act for Pakistan, as India and the United
States lose their tolerance for Pakistan’s Islamist militant franchise and the
state’s loss of control over that franchise.
For updates
click homepage here